Systematic Sampling
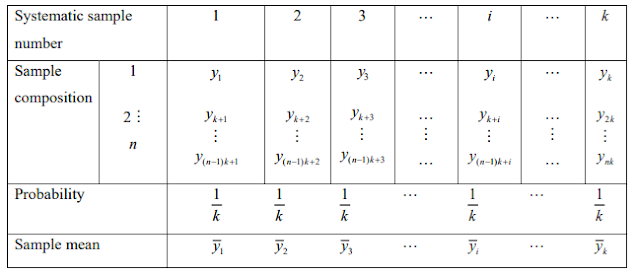
Unit 2: Other sampling Methods 2.1 Systematic Sampling The systematic sampling technique is operationally more convenient than simple random sampling. It also ensures, at the same time that each unit has an equal probability of inclusion in the sample. In this method of sampling, the first unit is selected with the help of random numbers, and the remaining units are selected automatically according to a predetermined pattern. This method is known as systematic sampling. Suppose the N units in the population are numbered 1 to N in some order. Suppose further that N is expressible as a product of two integers n and k, so that N=nk. To draw a sample of size n: 1. Select a random number between 1 and k. 2. Suppose it is i. 3. Select the first unit, whose serial number is i. 4. Select every k th unit after i th unit. The sample will contain I, i+k, i+2k,i+3k,.....,i+(n-1)k serial number units. Thus, the first unit is selected at...
